- Build and deployment variables
- Database variables
- Job-skipping variables
- Configure application secret variables
- Update application secrets
- Configure replica variables
- Deploy policy for staging and production environments
- Deploy policy for canary environments
- Incremental rollout to production
- Timed incremental rollout to production
CI/CD variables
Use CI/CD variables to set up the Auto DevOps domain, provide a custom Helm chart, or scale your application.
Build and deployment variables
Use these variables to customize and deploy your build.
| CI/CD variable | Description |
|---|---|
ADDITIONAL_HOSTS
| Fully qualified domain names specified as a comma-separated list that are added to the Ingress hosts. |
<ENVIRONMENT>_ADDITIONAL_HOSTS
| For a specific environment, the fully qualified domain names specified as a comma-separated list that are added to the Ingress hosts. This takes precedence over ADDITIONAL_HOSTS.
|
AUTO_BUILD_IMAGE_VERSION
| Customize the image version used for the build job. See list of versions.
|
AUTO_DEPLOY_IMAGE_VERSION
| Customize the image version used for Kubernetes deployment jobs. See list of versions. |
AUTO_DEVOPS_ATOMIC_RELEASE
| Auto DevOps uses --atomic for Helm deployments by default. Set this variable to false to disable the use of --atomic
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_BUILD_IMAGE_CNB_BUILDER
| The builder used when building with Cloud Native Buildpacks. The default builder is heroku/buildpacks:22. More details.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_BUILD_IMAGE_EXTRA_ARGS
| Extra arguments to be passed to the docker build command. Using quotes doesn’t prevent word splitting. More details.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_BUILD_IMAGE_FORWARDED_CI_VARIABLES
| A comma-separated list of CI/CD variable names to be forwarded to the build environment (the buildpack builder or docker build).
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_BUILD_IMAGE_CNB_PORT
| In GitLab 15.0 and later, port exposed by the generated Docker image. Set to false to prevent exposing any ports. Defaults to 5000.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_BUILD_IMAGE_CONTEXT
| Used to set the build context directory for Dockerfile and Cloud Native Buildpacks. Defaults to the root directory. |
AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART
| Helm Chart used to deploy your apps. Defaults to the one provided by GitLab. |
AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART_REPOSITORY
| Helm Chart repository used to search for charts. Defaults to https://charts.gitlab.io.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART_REPOSITORY_NAME
| Used to set the name of the Helm repository. Defaults to gitlab.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART_REPOSITORY_USERNAME
| Used to set a username to connect to the Helm repository. Defaults to no credentials. Also set AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART_REPOSITORY_PASSWORD.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART_REPOSITORY_PASSWORD
| Used to set a password to connect to the Helm repository. Defaults to no credentials. Also set AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART_REPOSITORY_USERNAME.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART_REPOSITORY_PASS_CREDENTIALS
| Set to a non-empty value to enable forwarding of the Helm repository credentials to the chart server when the chart artifacts are on a different host than repository. |
AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART_REPOSITORY_INSECURE
| Set to a non-empty value to add a --insecure-skip-tls-verify argument to the Helm commands. By default, Helm uses TLS verification.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART_CUSTOM_ONLY
| Set to a non-empty value to use only a custom chart. By default, the latest chart is downloaded from GitLab. |
AUTO_DEVOPS_CHART_VERSION
| Set the version of the deployment chart. Defaults to the latest available version. |
AUTO_DEVOPS_COMMON_NAME
| From GitLab 15.5, set to a valid domain name to customize the common name used for the TLS certificate. Defaults to le-$CI_PROJECT_ID.$KUBE_INGRESS_BASE_DOMAIN. Set to false to not set this alternative host on the Ingress.
|
AUTO_DEVOPS_DEPLOY_DEBUG
| If this variable is present, Helm outputs debug logs. |
AUTO_DEVOPS_ALLOW_TO_FORCE_DEPLOY_V<N>
| From auto-deploy-image v1.0.0, if this variable is present, a new major version of chart is forcibly deployed. For more information, see Ignore warnings and continue deploying. |
BUILDPACK_URL
| A full Buildpack URL. Must point to a URL supported by Pack. |
CANARY_ENABLED
| Used to define a deploy policy for canary environments. |
BUILDPACK_VOLUMES
| Specify one or more Buildpack volumes to mount. Use a pipe | as list separator.
|
CANARY_PRODUCTION_REPLICAS
| Number of canary replicas to deploy for Canary Deployments in the production environment. Takes precedence over CANARY_REPLICAS. Defaults to 1.
|
CANARY_REPLICAS
| Number of canary replicas to deploy for Canary Deployments. Defaults to 1. |
CI_APPLICATION_REPOSITORY
| The repository of container image being built or deployed, $CI_APPLICATION_REPOSITORY:$CI_APPLICATION_TAG. For more details, read Custom container image.
|
CI_APPLICATION_TAG
| The tag of the container image being built or deployed, $CI_APPLICATION_REPOSITORY:$CI_APPLICATION_TAG. For more details, read Custom container image.
|
DAST_AUTO_DEPLOY_IMAGE_VERSION
| Customize the image version used for DAST deployments on the default branch. Should usually be the same as AUTO_DEPLOY_IMAGE_VERSION. See list of versions.
|
DOCKERFILE_PATH
| Allows overriding the default Dockerfile path for the build stage |
HELM_RELEASE_NAME
| Allows the helm release name to be overridden. Can be used to assign unique release names when deploying multiple projects to a single namespace.
|
HELM_UPGRADE_VALUES_FILE
| Allows the helm upgrade values file to be overridden. Defaults to .gitlab/auto-deploy-values.yaml.
|
HELM_UPGRADE_EXTRA_ARGS
| Allows extra options in helm upgrade commands when deploying the application. Using quotes doesn’t prevent word splitting.
|
INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE
| If present, can be used to enable an incremental rollout of your application for the production environment. Set to manual for manual deployment jobs or timed for automatic rollout deployments with a 5 minute delay each one.
|
K8S_SECRET_*
| Any variable prefixed with K8S_SECRET_ is made available by Auto DevOps as environment variables to the deployed application.
|
KUBE_CONTEXT
| Can be used to select a context to use from KUBECONFIG. When KUBE_CONTEXT is blank, the default context in KUBECONFIG (if any) is used. A context must be selected when used with the agent for Kubernetes.
|
KUBE_INGRESS_BASE_DOMAIN
| Can be used to set a domain per cluster. See cluster domains for more information. |
KUBE_NAMESPACE
| The namespace used for deployments. When using certificate-based clusters, this value should not be overwritten directly. |
KUBECONFIG
| The kubeconfig to use for deployments. User-provided values take priority over GitLab-provided values. |
PRODUCTION_REPLICAS
| Number of replicas to deploy in the production environment. Takes precedence over REPLICAS and defaults to 1. For zero-downtime upgrades, set to 2 or greater.
|
REPLICAS
| Number of replicas to deploy. Defaults to 1. Change this variable instead of modifying replicaCount.
|
ROLLOUT_RESOURCE_TYPE
| Allows specification of the resource type being deployed when using a custom Helm chart. Default value is deployment.
|
ROLLOUT_STATUS_DISABLED
| Used to disable rollout status check because it does not support all resource types, for example, cronjob.
|
STAGING_ENABLED
| Used to define a deploy policy for staging and production environments. |
TRACE
| Set to any value to make Helm commands produce verbose output. You can use this setting to help diagnose Auto DevOps deployment problems. |
Database variables
{{< alert type=”warning” >}}
From GitLab 16.0, POSTGRES_ENABLED is no longer set by default.
{{< /alert >}}
Use these variables to integrate CI/CD with PostgreSQL databases.
| CI/CD variable | Description |
|---|---|
DB_INITIALIZE
| Used to specify the command to run to initialize the application’s PostgreSQL database. Runs inside the application pod. |
DB_MIGRATE
| Used to specify the command to run to migrate the application’s PostgreSQL database. Runs inside the application pod. |
POSTGRES_ENABLED
| Whether PostgreSQL is enabled. Set to true to enable the automatic deployment of PostgreSQL.
|
POSTGRES_USER
| The PostgreSQL user. Defaults to user. Set it to use a custom username.
|
POSTGRES_PASSWORD
| The PostgreSQL password. Defaults to testing-password. Set it to use a custom password.
|
POSTGRES_DB
| The PostgreSQL database name. Defaults to the value of $CI_ENVIRONMENT_SLUG. Set it to use a custom database name.
|
POSTGRES_VERSION
| Tag for the postgres Docker image to use. Defaults to 9.6.16 for tests and deployments. If AUTO_DEVOPS_POSTGRES_CHANNEL is set to 1, deployments uses the default version 9.6.2.
|
POSTGRES_HELM_UPGRADE_VALUES_FILE
| When using auto-deploy-image v2, this variable allows the helm upgrade values file for PostgreSQL to be overridden. Defaults to .gitlab/auto-deploy-postgres-values.yaml.
|
POSTGRES_HELM_UPGRADE_EXTRA_ARGS
| When using auto-deploy-image v2, this variable allows extra PostgreSQL options in helm upgrade commands when deploying the application. Using quotes doesn’t prevent word splitting.
|
POSTGRES_CHART_REPOSITORY
| Helm Chart repository used to search for PostgreSQL chart. Defaults to https://raw.githubusercontent.com/bitnami/charts/eb5f9a9513d987b519f0ecd732e7031241c50328/bitnami.
|
POSTGRES_CHART_VERSION
| Helm Chart version used for PostgreSQL chart. Defaults to 8.2.1.
|
Job-skipping variables
Use these variables to skip specific types of CI/CD jobs. When skipped, the CI/CD jobs don’t get created or run.
| Job name | CI/CD variable | GitLab version | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
.fuzz_base
| COVFUZZ_DISABLED
|
Read more about how .fuzz_base provide capability for your own jobs. The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
apifuzzer_fuzz
| API_FUZZING_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
build
| BUILD_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
build_artifact
| BUILD_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
brakeman-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
canary
| CANARY_ENABLED
| This manual job is created if the variable is present. | |
code_intelligence
| CODE_INTELLIGENCE_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
code_quality
| CODE_QUALITY_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
container_scanning
| CONTAINER_SCANNING_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
dast
| DAST_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
dast_environment_deploy
|
DAST_DISABLED_FOR_DEFAULT_BRANCH or DAST_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
dependency_scanning
| DEPENDENCY_SCANNING_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
flawfinder-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
gemnasium-dependency_scanning
| DEPENDENCY_SCANNING_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
gemnasium-maven-dependency_scanning
| DEPENDENCY_SCANNING_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
gemnasium-python-dependency_scanning
| DEPENDENCY_SCANNING_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
kubesec-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
license_management
| LICENSE_MANAGEMENT_DISABLED
| GitLab 12.7 and earlier | If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. Job deprecated from GitLab 12.8 |
license_scanning
| LICENSE_MANAGEMENT_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true". Job deprecated from GitLab 15.9
| |
load_performance
| LOAD_PERFORMANCE_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
nodejs-scan-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
performance
| PERFORMANCE_DISABLED
| GitLab 13.12 and earlier | Browser performance. If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. Replaced by browser_performance.
|
browser_performance
| BROWSER_PERFORMANCE_DISABLED
| Browser performance. If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. Replaces performance.
| |
phpcs-security-audit-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
pmd-apex-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
review
| REVIEW_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
review:stop
| REVIEW_DISABLED
| Manual job. If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
secret_detection
| SECRET_DETECTION_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
secret_detection_default_branch
| SECRET_DETECTION_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
semgrep-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
sobelow-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
stop_dast_environment
|
DAST_DISABLED_FOR_DEFAULT_BRANCH or DAST_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
spotbugs-sast
| SAST_DISABLED
| The job isn’t created if the value is "true".
| |
test
| TEST_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. | |
staging
| STAGING_ENABLED
| The job is created if the variable is present. | |
stop_review
| REVIEW_DISABLED
| If the variable is present, the job isn’t created. |
Configure application secret variables
Some deployed applications require access to secret variables.
Auto DevOps detects CI/CD variables starting with K8S_SECRET_,
and makes them available to the deployed application as
environment variables.
Prerequisites:
- The variable value must be a single line.
To configure secret variables:
- On the left sidebar, select Search or go to and find your project.
- Select Settings > CI/CD.
- Expand Variables.
- Create a CI/CD variable with the prefix
K8S_SECRET_. For example, you can create a variable calledK8S_SECRET_RAILS_MASTER_KEY. - Run an Auto DevOps pipeline, either by manually creating a new pipeline or by pushing a code change to GitLab.
Kubernetes secrets
Auto DevOps pipelines use your application secret variables to
populate a Kubernetes secret. This secret is unique per environment.
When deploying your application, the secret is loaded as environment
variables in the container running the application. For example, if
you create a secret called K8S_SECRET_RAILS_MASTER_KEY, your
Kubernetes secret might look like:
$ kubectl get secret production-secret -n minimal-ruby-app-54 -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
RAILS_MASTER_KEY: MTIzNC10ZXN0
kind: Secret
metadata:
creationTimestamp: 2018-12-20T01:48:26Z
name: production-secret
namespace: minimal-ruby-app-54
resourceVersion: "429422"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/minimal-ruby-app-54/secrets/production-secret
uid: 57ac2bfd-03f9-11e9-b812-42010a9400e4
type: Opaque
Update application secrets
Environment variables are generally immutable in a Kubernetes pod. If you update an application secret and then manually create a new pipeline, running applications do not receive the updated secret.
To update application secrets, either:
- Push a code update to GitLab to force the Kubernetes deployment to recreate pods.
- Manually delete running pods to cause Kubernetes to create new pods with updated secrets.
Variables with multi-line values are not supported due to limitations with the Auto DevOps scripting environment.
Configure replica variables
Add replica variables when you want to scale your deployments:
- Add a replica variable as a project CI/CD variable.
-
To scale your application, redeploy it.
{{< alert type=”warning” >}}
Do not scale your application using Kubernetes directly. Helm might not detect the change, and subsequent deployments with Auto DevOps can undo your changes.
{{< /alert >}}
Custom replica variables
You can create custom replica variables with the format <TRACK>_<ENV>_REPLICAS:
-
<TRACK>is the all-caps value of thetrackKubernetes label set in the Helm Chart app definition. Iftrackis not set, omit<TRACK>from the custom variable. -
<ENV>is the all-caps environment name of the deploy job set in.gitlab-ci.yml.
For example, if the environment is qa and the track is
foo, create an environment variable called FOO_QA_REPLICAS:
QA testing:
stage: deploy
environment:
name: qa
script:
- deploy foo
The track foo must be defined in the application’s Helm chart.
For example:
replicaCount: 1
image:
repository: gitlab.example.com/group/project
tag: stable
pullPolicy: Always
secrets:
- name: gitlab-registry
application:
track: foo
tier: web
service:
enabled: true
name: web
type: ClusterIP
url: http://my.host.com/
externalPort: 5000
internalPort: 5000
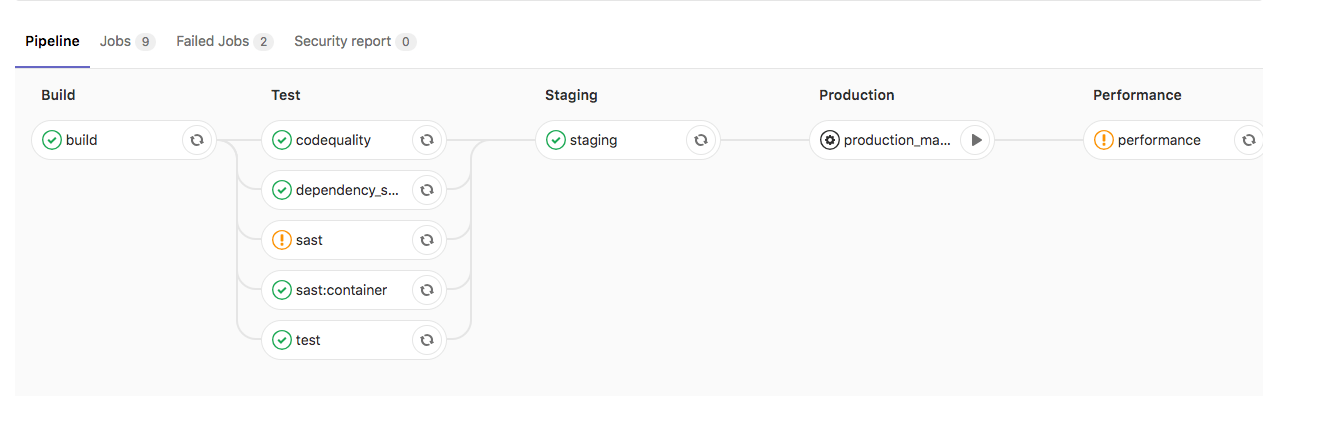
Deploy policy for staging and production environments
Auto DevOps typically uses continuous deployment, and pushes
automatically to the production environment whenever a new pipeline
runs on the default branch. To deploy to production manually, you can
use the STAGING_ENABLED CI/CD variable.
If you set STAGING_ENABLED, GitLab automatically deploys the
application to a staging environment. When you’re ready to deploy to
production, GitLab creates a production_manual job.
You can also enable manual deployment in your project settings.
Deploy policy for canary environments
{{< details >}}
- Tier: Premium, Ultimate
- Offering: GitLab.com, GitLab Self-Managed, GitLab Dedicated
{{< /details >}}
You can use a canary environment before deploying any changes to production.
If you set CANARY_ENABLED, GitLab creates two manual jobs:
-
canary- Deploys the application to the canary environment. -
production_manual- Deploys the application to production.
Incremental rollout to production
{{< details >}}
- Tier: Premium, Ultimate
- Offering: GitLab.com, GitLab Self-Managed, GitLab Dedicated
{{< /details >}}
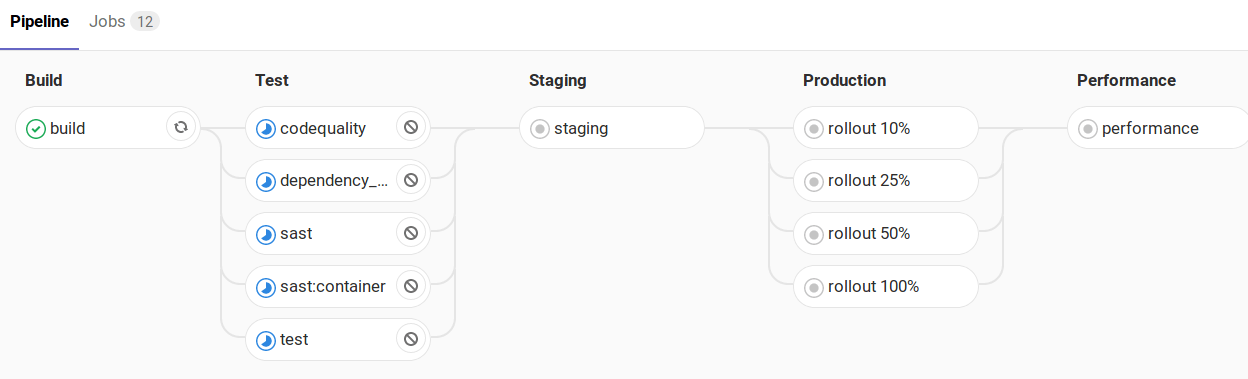
Use an incremental rollout to continuously deploy your application, starting with only a few pods. You can increase the number of pods manually.
You can enable manual deployment in your project settings,
or by setting INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE to manual.
If you set INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE to manual, GitLab creates four
manual jobs:
rollout 10%rollout 25%rollout 50%rollout 100%
The percentage is based on the REPLICAS CI/CD variable, and defines the number of
pods used for deployment. For example, if the value is 10 and you run the
10% rollout job, your application is deployed to only one pod.
You can run the rollout jobs in any order. To scale down, rerun a lower percentage job.
After you run the rollout 100% job, you cannot scale down, and must
roll back your deployment.
Example incremental rollout configurations
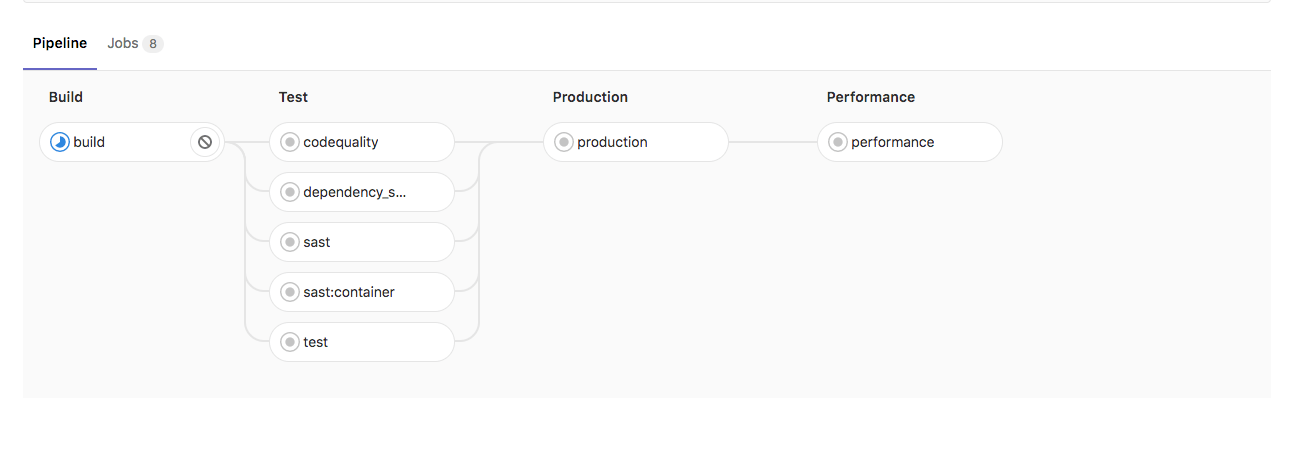
Without INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE and without STAGING_ENABLED:
Without INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE and with STAGING_ENABLED:
With INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE set to manual and without STAGING_ENABLED:
With INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE set to manual and with STAGING_ENABLED:
Timed incremental rollout to production
{{< details >}}
- Tier: Premium, Ultimate
- Offering: GitLab.com, GitLab Self-Managed, GitLab Dedicated
{{< /details >}}
Use a timed incremental rollout to continuously deploy your application, starting with only a few pods.
You can enable timed incremental deployment in your project settings,
or by setting the INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE CI/CD variable to timed.
If you set INCREMENTAL_ROLLOUT_MODE to timed, GitLab creates four jobs:
timed rollout 10%timed rollout 25%timed rollout 50%timed rollout 100%
There is a five-minute delay between jobs.